 WHAT IS MLD?
WHAT IS MLD?
This page details information about MLD, however more information and pricing can be found on our dedicated site
Manual Lymphatic Drainage is a specialised technique of gentle massage on the surface of the skin which helps the lymphatic system to work better. It consists of light rhythmical and calming hand movements which gently stretch the skin in specific directions stimulating the lymphatic system. The aim of MLD is to redirect fluid from congested areas towards healthy lymphatic’s where the fluid can be drained by normal routes back into the circulation. This pressure is applied evenly, repetitively and rhythmically which creates in the person being treated an incredibly deep relaxing feeling. These movements do not cause redness of the skin, neither do they cause any pain.
Margaret is now working with the Hivamat machine please click onto link (www.physiopod.co.uk) to find out how this wonderful machine helps in her treatments, especially with Lymphoedema patients.
HOW IT WORKS IN THE BODY
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM – reduces swelling and removes toxins, thus helps to reduce swollen ankles, tired puffy eyes and fluid retention due to pregnancy or pre menstrual syndrome. Invaluable in the treatment of lymphoedema.
NERVOUS SYSTEM – calms it down and has a mild pain relieving effect.
MUSCULAR SYSTEM – improves muscle tone. It can help to heal torn muscle and ligament fibres by reducing the inflammation after injury.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – it helps digestion by aiding the peristalsis action of the bowel.
IMMUNE SYSTEM – the lymphatic system makes cells called lymphocytes (antibodies) which help the body fight infection. These immune cells travel through the body faster in a functional lymphatic system.
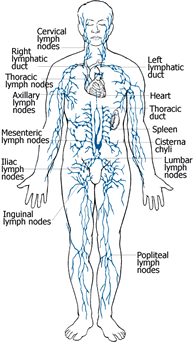
THE LYMPH SYSTEM
The lymphatic system is made up of a vast network of capillaries that transport the lymph (fluid). This fluid consists of water, plasma proteins, foreign substances i.e. ink, dust, bacteria and other waste products. The body’s defense cells known as antibodies are also carried in the lymph fluid.
The function of the lymphatics is to clear protein, water and waste from the tissues and to distribute antibodies to areas of the body where they are needed to fight infection.
Fluid accumulation in the tissues can be due to the absence, damage to, or obstruction of lymphatic vessels or nodes which will then affect the transporting capacity of the system. When the fluid builds up in the body to the point where it becomes too much for the lymphatics to drain it away, then oedema (swelling) occurs. It is similar to that of a river which has been dammed – water builds up behind the dam, overflows the banks of the river and if the ground does not drain properly it becomes waterlogged.
Lymph flows slowly upward through the body to the chest where it drains into the bloodstream through two large ducts. Lymph also flows down from the head and neck into this drainage site. Unlike the heart, the lymphatic system does not have a pump to move it along, its movements depend on factors such as natural pulsation of the lymph vessels, muscle contraction, respiration, arterial pulsation and massage with manual lymphatic drainage.
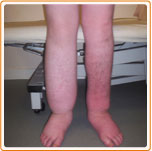
LYMPHOEDEMA
This happens due to the drainage routes of the lymphatic system becoming blocked or damaged and as a result lymph fluid accumulates in the tissues and swelling occurs. Also fibrosis (excess protein which causes hardness) can be present in the tissue and an increased risk of infection occurs. As a result of this fibrosis, the swelling increases, and can become more difficult to control. Lymphoedema is divided into two categories;
Primary: This is usually determined from birth and may be due to under development of the lymphatic system. It can affect infants or children, men or women at any age and is seen most frequently in the arms and legs.
Secondary: This can occur in treatment of cancer following surgery or radiotherapy where lymph nodes have been removed or damaged or scar tissue has formed and lymph drainage routes may be reduced. It can also occur as a result of infection, severe injury, burns or any other trauma.
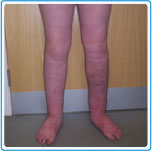
after treatment
TREATMENT FOR LYMPHOEDEMA
For MLD to be effective it is essential that the treatment time suits the illness. For large swellings or chronic health problems, 6-10 sessions (at least) 1 per day for 6-10 days consecutively is needed. Maintenance treatments after the initial treatment programme are recommended as lymphoedema is a lifelong condition. Maintenance could be 1 treatment per month or 2 to 4 times per year, depending on the condition.
In blocked lymph vessels, the lymph load which is rich in waste products must be pushed inch by inch through these blocked vessels to be filtered by the receiving lymph nodes. Any fibrosis which hinders flow must be treated specifically and so time must be spent to soften this and allow lymph fluid to pass through.
Once treatment has finished clients will be advised on proper compression garments to wear, also exercises will be given, advised on diet, travel and living with lymphoedema. A course of bandaging may be necessary to reduce the fluid in addition to MLD. If this is the case then a letter can be sent to your General Practitioner as bandages are available on prescription. Self massage techniques will also be shown for the patient to practise at home. 100,000 people in the UK may have lymphoedema. Studies have shown that some people with this condition feel anxious, depressed or isolated, but this treatment is very successful and the relief clients feel afterwards is absolutely amazing!
For more detailed information regarding a treatment plan for any illness, please phone the clinic and ask to speak to Margaret Taylor personally.